 Procedures For Soft Tissues/Gums (Cont’d):
Procedures For Soft Tissues/Gums (Cont’d):
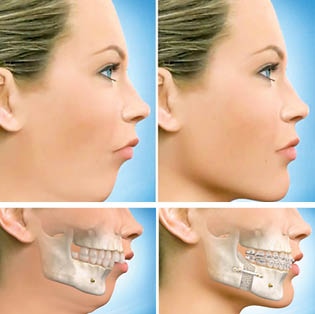
Surgical Procedures: Most film actors choose to undergo procedures to enhance their features – be it jaw narrowing/reshaping, obtaining high cheekbones, increasing the size of a small lower jaw, reducing an over-sized upper/lower jaw, to the simplest of all – Botox! Among the Parsi community a deficient or underdeveloped lower jaw is common. During childhood, it can be easily treated without surgery through ‘Dentofacial Orthopedics’ (as explained last week in PT). If not treated in childhood, the only solution is surgical enhancement of the jaws (as explained by the adjoining pictures)
Bleaching/ Tooth Whitening: Food and drink, smoking, age, trauma, medications – all may cause discoloration of teeth over time. Teeth-whitening is a simple process, where teeth stains are broken into smaller pieces, making the colour less concentrated, and your teeth brighter. But whitening does not work on all types of stains/discolorations. Bleaching is quite effective for teeth which have yellowed due to food stains but not as effective for discoloration due to medication.
Bleaching is done in three ways:
1) Whitening Toothpastes: Widely available over the counter, help in removing tooth stains. However misuse/overuse of these toothpastes can cause loss of enamel, leading to irreversible damage to teeth. Best not used on a regular basis.
2) In-Office Bleaching: This procedure called ‘Chairside Bleaching’ usually requires only one office visit. The dentist will apply either a protective gel to your gums or a rubber shield to protect your gums. Bleach is then applied to the teeth. A special light or laser might be used to enhance the action of the whitening agent.
3) At-Home Bleaching: Available in gel form and placed in a tray that fit your teeth. You may also use a whitening strip that sticks to your teeth. The concentration of the bleaching agent is lower than what your dentist would use in the office.
Bleaching itself lasts six to twelve months on an average and must not be done too frequently. Veneers can be considered as a permanent option.
Side effects of Teeth Whiteners: Some people may experience temporary tooth sensitivity, when the peroxide in the whitener gets through the enamel irritates the nerve of your tooth.
Procedures For Soft Tissues / Gums:
Gingivectomy/Gingivoplasty: These are gum contouring procedures which shape your gums to achieve a perfect esthetic look to the teeth. Beauty often lies in symmetry and this can be achieved by contouring the gingiva. Advanced clinics often use laser to do the same. In other conditions, grafting of gingiva can also be done to improve esthetics.
Depigmentation of Gingiva: Darkening of gingiva is due to melanin pigmentation and causes embarrassment to smile-conscious individuals. Cosmetic therapy is sought after, especially by fair-skinned people with moderate or severe gingival pigmentation, mostly in patients with a high smile line (gummy smile). ‘Gingival Depigmentation’ is performed whereby the gingival hyperpigmentation is removed or reduced by various techniques. It can be done surgically, chemically or by laser and lasts approximately for a year. The pigmentation never becomes as dark as the original.
Happy Smiling!
- દિકરી એટલે બીજી માં… - 20 April2024
- નાગપુરની બાઈ હીરાબાઈ એમ. મુલાનદરેમહેરનો ઇતિહાસ - 20 April2024
- વિશ્વ ભારતી સંસ્થાન દ્વારા રતિ વાડિયાનુંસન્માન કરવામાં આવ્યું - 20 April2024
