Everyone snores occasionally, and it’s usually not a matter of concern. However, snoring regularly at night can disrupt the quality of your sleep, leading to headaches, daytime fatigue, irritability, and increased health problems. And if your snoring keeps your partner awake, it could cause issues in your relationship. But you need to understand the root of a problem before you can solve it. So, what causes a person to snore?
Snoring takes place when the air can’t move freely through your nose and throat when you’re asleep. This makes the surrounding tissues vibrate, which produce the snoring sound. Snorers are usually known to have excess throat and nasal tissue or “floppy” tissue that is more prone to vibrate. Sometimes, the position of your tongue can also get in the way of smooth breathing. Since people snore for different reasons, let’s understand the causes behind snoring, so that you can find the right solutions to a quieter, deeper sleep.
Common Causes of Snoring:
- Age:As you reach middle age and beyond, your throat becomes narrower, and the muscle tone in your throat decreases, causing disturbance in the air flow.
- Being Overweight/Unfit: Fatty tissue and poor muscle tone contribute to snoring. Exercising and weight loss could help end snoring.
- Your Built: Men have narrower air passages than women and are therefore more likely to snore. A narrow throat, a cleft palate, enlarged adenoids, and other physical attributes that contribute to snoring are often hereditary.
- Nasal / Sinus problems:Blocked airways or a stuffy nose makes inhalation difficult, creating a vacuum in the throat which causes snoring.
- Alcohol, Smoking, Medications: Alcohol intake, smoking, and certain medications, especially sedatives, increase muscle relaxation leading to snoring.
- Sleep Posture:Sleeping flat on your back causes the flesh of your throat to relax and block the airway.
Sometimes, snoring could indicate ‘Sleep Apnea’, a serious sleep disorder, where your breathing is briefly interrupted numerous times each night. See a doctor if you are experiencing these three main conditions – You snore loudly and heavily and are tired through the day; While sleeping you stop breathing, and gasp or choke; and, You fall asleep at inappropriate times, such as during a conversation or a meal.
Remedies To Stop Snoring:
The numerous anti-snoring devices available in the market today are more confusing than anything else. Unfortunately, many of these devices are not backed up by research, or they work by simply keeping you awake at night! But don’t lose hope because there are a number of proven techniques that can help cure snoring. Not every remedy is right for every person, so putting a stop to your snoring will require patience, effort and the willingness to experiment with different harmless but effective solutions, as under:
- Change Your Sleeping Position: Elevating your head four inches eases breathing and encourages your tongue and jaw to move forward. There are specifically designed pillows available to help prevent snoring by making sure your neck muscles are not crimped.
- Sleep On Your Side, Not On Your Back.
- Clear Your Nasal Passage: If you have a stuffy nose, rinse sinuses with saline before bed. Using a nasal decongestant, nasal strips or steam inhalation, will help you breathe more easily while sleeping.
- Use Allergy Medication: if you have allergies. Reduce dust mites and keep an air purifier. Keep your bed and sleeping area free of pet dander.
- Keep Bedroom Air Moist:Dry air irritates nasal membranes and the throat, so if swollen nasal tissues are the problem, a humidifier may help.
- Introduce Healthy Lifestyle Changes in your daily routine, like:
- Losing Excess Weight:This reduces fatty tissue in the back of the throat and decrease, or even stop, snoring.
- Reduce/Quit Smoking:Smokers are snorers. Smoking irritates the membranes in the nose and throat which can block the airways and cause snoring.
- Avoid Alcohol and Sedatives:These relax the muscles in the throat and interfere with breathing. Sometimes, prescription medications, like sleeping pills, encourage a deeper level of sleep, which can make snoring worse.
- Take Heed Of Your Meals Before Sleeping: Research shows that eating large meals or consuming certain foods such as dairy right before bedtime can make snoring worse.
- Exercise: Any form of working out reduces snoring, even if it doesn’t lead to weight loss. That’s because when you tone muscles in your body, such as your arms, legs, and abs, this leads to toning the muscles in your throat, which in turn lead to less snoring.
- Practice Anti-Snoring Throat Exercises: Research has shown that by pronouncing certain vowel sounds and curling the tongue in specific ways, muscles in the upper respiratory tract are strengthened and therefore reduce snoring. Try the following six exercises known to help:
- Repeat each vowel (a-e-i-o-u) loudly for three minutes, a few times a day.
- Place the tip of your tongue behind your top front teeth. Slide your tongue backwards for three minutes a day.
- Close your mouth and purse your lips. Hold for 30 seconds.
- With your mouth open, move your jaw to the right and hold for 30 seconds. Repeat on the left side.
- With your mouth open, contract the muscle at the back of your throat repeatedly for 30 seconds. Tip: Look in the mirror to see the uvula (“the hanging ball”) move up and down.
- A fun exercise is to simply spend time singing. Singing increases muscle control in the throat and soft palate, reducing snoring caused by lax muscles.
When these self-help techniques do not work, you could try an Anti-Snoring Mouth Appliance or opt for medical treatment for snoring. Do this only under professional guidance from your General Physician or Otolaryngologist (Ear, Nose, and Throat or ENT doctor). Medical cures for snoring include:
- Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP):To keep your airway open during sleep, a machine at your bedside blows pressurized air into a mask that you wear over your nose or face.
- Laser-Assisted Uvulopalatoplasty (LAUP):To shorten the uvula (the hanging soft tissue at the back of the throat) and to make small cuts in the soft palate either side. As the cuts heal, the surrounding tissues stiffen to prevent the vibrations that trigger snoring.
- Palatal Implants (The Pillar Procedure): Involves inserting small plastic implants into the soft palate which help prevent its collapse to avoid snoring.
- Somnoplasty:Using low levels of radiofrequency heat to remove tissues of the uvula and soft palate that vibrate during snoring. This is a 30-minute procedure and is performed under local anaesthesia.
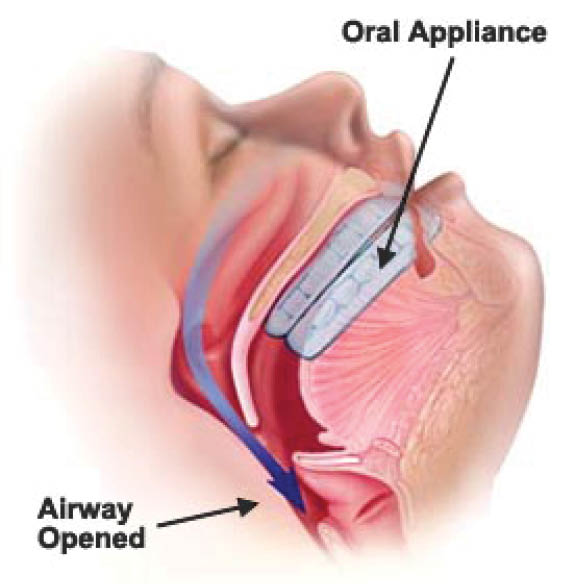
- Custom-fitted Dental Devices and Lower Jaw-Positioners: To help open your airway by bringing your lower jaw or your tongue forward during sleep. This is done by dentists who specializes in these devices.
- Other Surgical Procedures:Such as Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP), Thermal Ablation Palatoplasty (TAP), Tonsillectomy, and Adenoidectomy, which increase the size of your airway by the surgical removal of tissues or by correcting other abnormalities.
- દિકરી એટલે બીજી માં… - 20 April2024
- નાગપુરની બાઈ હીરાબાઈ એમ. મુલાનદરેમહેરનો ઇતિહાસ - 20 April2024
- વિશ્વ ભારતી સંસ્થાન દ્વારા રતિ વાડિયાનુંસન્માન કરવામાં આવ્યું - 20 April2024
