Genetic Susceptibility, Symptoms, Strategies For Prevention
 Alzheimer’s disease is a relentless and debilitating brain disorder affecting millions worldwide. As the leading cause of dementia, it presents a significant health challenge in ageing populations. According to the Alzheimer’s Association, about 5.3 million Indians are currently living with this condition, and the numbers continue to rise. Despite its devastating impact, there is hope in understanding genetic susceptibility, recognizing early symptoms, and implementing effective prevention strategies. By understanding this ailment, we can take proactive steps to reclaim our health and well-being.
Alzheimer’s disease is a relentless and debilitating brain disorder affecting millions worldwide. As the leading cause of dementia, it presents a significant health challenge in ageing populations. According to the Alzheimer’s Association, about 5.3 million Indians are currently living with this condition, and the numbers continue to rise. Despite its devastating impact, there is hope in understanding genetic susceptibility, recognizing early symptoms, and implementing effective prevention strategies. By understanding this ailment, we can take proactive steps to reclaim our health and well-being.
What Is Alzheimer’s Disease?
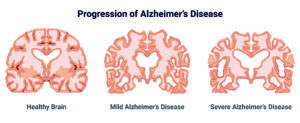
Alzheimer’s disease is a complex neurological disorder that is characterized by progressive cognitive decline and memory loss. While the exact mechanisms of this condition are still being studied, it is believed to be caused by an abnormal accumulation of proteins in the brain that form plaque, which ends up disrupting communication between brain cells.
Ultimately, this degeneration results in loss of cognitive function and the ability to perform daily activities, like driving or brushing your teeth. In functional medicine, Alzheimer’s is considered the result of various genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors, built up over time.
Early Signs Of Alzheimer’s Disease:
- Word mix-ups during a speech
- Misplacing items in unusual locations
- Experiencing disorientation in familiar surroundings
- Changes in mood or behaviour
- Difficulty focusing for extended periods
- Repeatedly asking the same questions
- Taking longer to perform routine tasks
- Experiencing general cognitive fog
Common Symptoms Of Alzheimer’s:
Recognizing early signs of Alzheimer’s is crucial for timely intervention and management. The disease progresses gradually, and symptoms may initially appear mild but become more pronounced over time:
Memory Loss: Difficulty recalling recent events, conversations, or appointments is often one of the first signs of Alzheimer’s. Individuals repeatedly ask the same questions or rely heavily on notes and reminders.
Disorientation and Confusion: People with Alzheimer’s may become disoriented, lose track of time, or get confused about their location, even in familiar places.
Challenges in Problem-Solving / Planning: Alzheimer’s can impact an individual’s ability to make decisions, solve problems, or plan daily activities.
Difficulty Performing Familiar Tasks: Routine tasks such as cooking, driving, or managing finances, may become challenging for individuals with Alzheimer’s.
Changes in Mood and Personality: Mood swings, increased irritability, and withdrawal from social activities are common emotional changes associated with the disease.
Trouble with Language: Individuals may struggle to find the right words or follow conversations, making communication difficult.
Genetic Susceptibility To Alzheimer’s:
While the exact cause of Alzheimer’s remains elusive, researchers have identified certain genetic factors that can increase an individual’s susceptibility to the disease. Other genetic factors, such as mutations, also play a role in the early-onset familial form of Alzheimer’s, which is relatively rare and tends to appear before the age of 65. Nonetheless, majority of Alzheimer’s cases are considered late-onset, where a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors contribute to the disease’s development.
Natural Remedies To Prevent Alzheimer’s Disease:
Research suggests that lifestyle factors significantly impact an individual’s risk of developing the disease. Implementing certain preventive strategies could promote brain health and reduce the risk of cognitive decline. These could include:
- Adopting ‘Brain-Healthy’ Diet: Emphasize a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, healthy fats, and lean proteins. The Mediterranean diet, in particular, has been associated with brain health due to its emphasis on heart-healthy foods and antioxidants. Limit your sugar intake and add more healthy fats to your diet.
- 2. Regular Physical Activity: has been linked to improved brain health and cognitive function. Aim for a mix of aerobic exercises, strength training, and activities that challenge your brain, such as puzzles and games.
- Staying Mentally And Socially Active: Engaging in mentally stimulating activities, like reading, learning new skills, or playing musical instruments, can help keep the brain sharp. Social interactions and maintaining a strong support network are also beneficial.
- Prioritizing Quality Sleep: Aim for 7 to 9 hours of restful sleep each night, as sleep plays a vital role in brain health and cognitive function.
- Managing Stress: Chronic stress contributes to cognitive decline. Practice stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature.
- 6. Limiting Alcohol And Avoiding Smoking: Excessive alcohol consumption and smoking have been linked to an increased risk of cognitive decline. Limiting alcohol intake and avoiding smoking are essential for brain health.
- 7. Work On Your Gut Health: To improve your brain health, it’s essential to prioritize the well-being of your ‘second brain’ – your gut. In my practice, I frequently discuss the gut-brain connection, emphasizing the crucial bi-directional relationship between these two vital systems in maintaining cognitive function. The health of your gut significantly impacts your brain, and vice versa.
- Genetic Testing: I consistently advise individuals to gather as much health information as they can. Genetic testing can help identify any genetic mutations that may raise the risk of developing Alzheimer’s. Armed with knowledge, you can create a focused plan of action that prioritizes brain support and addresses potential concerns proactively. I recommend getting this test for those with a family history of dementia or Alzheimer’s.
While a cure for Alzheimer’s remains elusive, understanding your genetic risk and prioritizing brain health can significantly contribute to prevention as you age. These strategies can also be valuable if you are in the early stages of the condition. If you are encountering any initial signs of Alzheimer’s or seeking to enhance brain health naturally, consider scheduling a consultation with your healthcare expert.
PROTECT YOURSELF FROM CONJUNCTIVITIS!
India is battling a surge in conjunctivitis/eye flu cases over the past few weeks. Conjunctivitis, commonly known as pink eye, is an inflammation of the conjunctiva (the thin, transparent layer that covers the white part of the eye and the inside of the eyelids). It is highly contagious and is caused by viruses, bacteria, allergies, or irritants. Here are some tips to protect yourself from conjunctivitis:
- Practice Good Hygiene: Wash your hands frequently with soap and water, especially before touching your eyes or face. Avoid touching or rubbing your eyes, as this can spread the infection.
- Avoid Sharing Personal Items: Do not share towels, washcloths, pillowcases, eye drops, or makeup with others, as these items can easily transfer infection.
- Keep Hands Away from Your Eyes: Consciously keep your hands away from your eyes – this reduces the risk of spreading contagion.
- Avoid Close Contact With Infected Individuals: As this is a very contagious disease, avoid close contact with those who are infected till it has cleared up.
- Use Protective Eyewear: If your eyes are exposed to potential irritants / contaminants (through swimming or working with chemicals), wear protective goggles or eyewear. Ensure to sanitize it before next use. Do not share the eyewear.
- Maintain Clean Contact Lenses: If you wear contact lenses, follow proper hygiene and cleaning procedures. Replace disposable lenses as recommended by your eye care professional.
- Avoid Allergens: If you have allergic conjunctivitis, avoid triggers like pollen, dust, pet dander, or certain cosmetics.
- Clean Eyeglasses: Regularly clean your eyeglasses using the lens-cleaning solution or mild soap and water. Dirty glasses harbour bacteria and irritants.
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Eating a balanced diet, staying hydrated, and getting enough sleep can support overall eye health and reduce the risk of infections.
- Seek Medical Attention: If you experience symptoms of conjunctivitis, such as redness, itching, swelling, or discharge from the eyes, consult an eye care professional promptly, to avail timely and appropriate treatment.
- Strengthen Your Constitution This Republic Day! - 25 January2025
- Become A ‘Smart Sipper’ This Festive Season! - 28 December2024
- Beat The Winter Sniffles - 23 November2024
